Building an AI-Powered Job Matcher: From Web Scraping to LLM Tagging, Vector Search & Analytics
Why
Recruiters and candidates face the same challenge: how to connect the right person with the right role. Traditional job boards reduce this to keyword searches, but keywords alone don’t capture intent, context, or skills. With today’s AI tooling, we can do better.
In this article, we’ll build a job matching platform that scrapes postings from the web, enriches them with AI tags, and matches them against resumes or natural-language queries. The solution combines Java Spring Boot, LangChain, LLMs, Weaviate, ClickHouse, Temporal, Selenium, PostgreSQL, and DigitalOcean Spaces.
Use Case
Imagine a platform that pulls jobs from dozens of sources, normalizes them, and recommends best-fit roles to candidates. Users can:
- Upload their resume to get tailored matches.
- Search naturally (“Software engineer jobs in Amsterdam paying 100K+”).
- Get recommendations powered by embeddings, not just keywords.
Requirements
Functional:
- Scrape jobs from multiple job boards.
- Enrich jobs with AI tags and embeddings.
- Allow semantic search via resumes or natural queries.
- Store and retrieve resumes securely.
Non-Functional:
- Resilient orchestration with retries.
- Fast hybrid search (semantic + filters).
- Real-time analytics on usage and search funnels.
- Data privacy compliance (GDPR-ready).
Key Considerations
- Selenium handles job boards without APIs.
- Temporal orchestrates scraping and enrichment workflows.
- LangChain + LLM extract skills, salaries, and seniority.
- Weaviate provides semantic + keyword search.
- ClickHouse stores analytics for insights.
- DigitalOcean Spaces stores raw resumes.
High Level Architecture
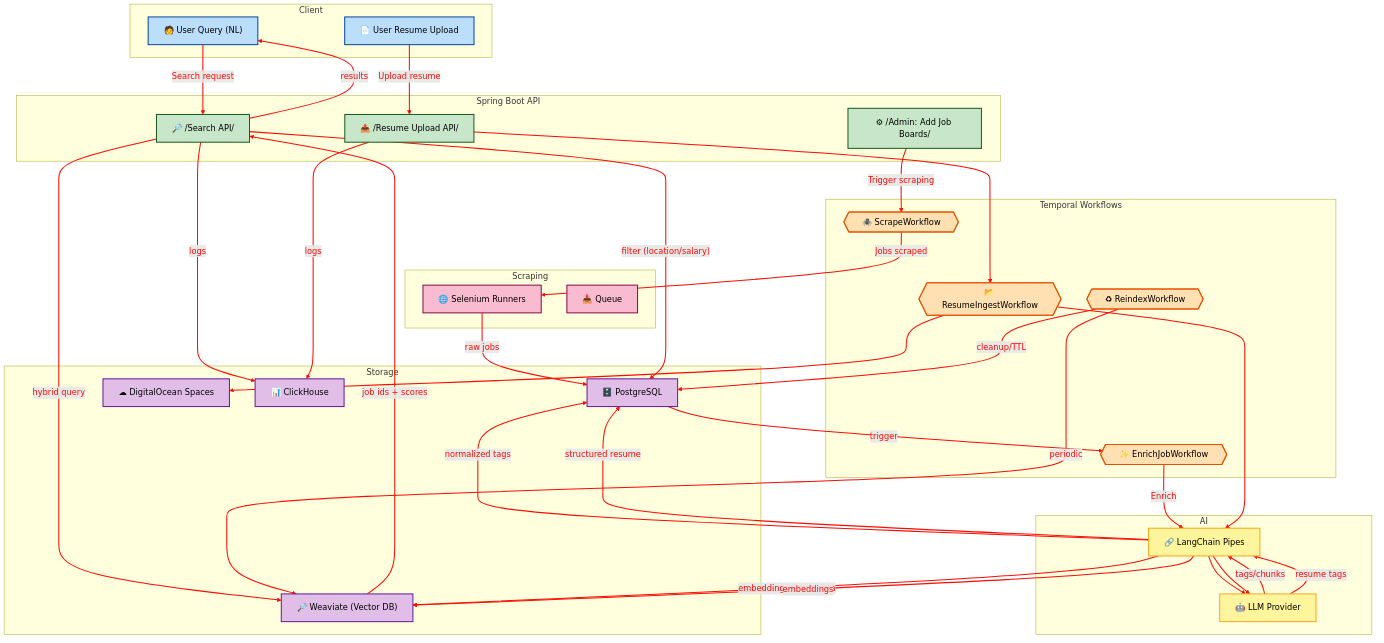
Implementation
Data Models (Postgres)
CREATE TABLE job_post
(
id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
title TEXT NOT NULL,
company TEXT,
location_city TEXT,
salary_min NUMERIC,
salary_max NUMERIC,
currency CHAR(3),
seniority TEXT,
description_md TEXT,
tags JSONB,
posted_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
status TEXT NOT NULL DEFAULT 'active'
);
CREATE TABLE resume
(
id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
user_id UUID,
file_url TEXT NOT NULL,
content_text TEXT,
tags JSONB,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL DEFAULT now()
);
CREATE TABLE search_session
(
id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
user_id UUID,
query_text TEXT NOT NULL,
extracted_filters JSONB,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL DEFAULT now()
);Vector Models (Weaviate)
{
"classes": [
{
"class": "JobPost",
"vectorizer": "text2vec-openai",
"properties": [
{
"name": "title",
"dataType": [
"text"
]
},
{
"name": "locationCity",
"dataType": [
"text"
]
},
{
"name": "salaryMin",
"dataType": [
"number"
]
},
{
"name": "salaryMax",
"dataType": [
"number"
]
},
{
"name": "tags",
"dataType": [
"text[]"
]
}
]
},
{
"class": "Resume",
"vectorizer": "text2vec-openai",
"properties": [
{
"name": "userId",
"dataType": [
"text"
]
},
{
"name": "contentText",
"dataType": [
"text"
]
},
{
"name": "tags",
"dataType": [
"text[]"
]
}
]
}
]
}Analytics (ClickHouse)
CREATE TABLE analytics.events
(
event_time DateTime,
event_type String,
user_id Nullable(String),
query_text Nullable(String),
query_tags Nullable(JSON),
job_id Nullable(String),
resume_id Nullable(String)
) ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY (event_time, event_type);Workflows (Temporal)
@WorkflowInterface
public interface ScrapeWorkflow {
@WorkflowMethod
void runScrape(UUID jobBoardId);
}
@WorkflowInterface
public interface EnrichJobWorkflow {
@WorkflowMethod
void enrich(UUID jobId);
}
@WorkflowInterface
public interface ResumeIngestWorkflow {
@WorkflowMethod
void ingest(UUID resumeId);
}API Endpoints (Spring Boot)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/jobs")
public class JobController {
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<JobPost> searchJobs(@RequestParam String query) {
// 1. Extract tags with LLM
// 2. Query Weaviate with hybrid search
// 3. Filter results in Postgres
return jobService.search(query);
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/resumes")
public class ResumeController {
@PostMapping("/upload")
public Resume uploadResume(@RequestParam MultipartFile file, @RequestParam UUID userId) {
// 1. Store file in DigitalOcean Spaces
// 2. Parse with Apache Tika
// 3. Enrich with LLM
// 4. Index in Weaviate & Postgres
return resumeService.ingest(file, userId);
}
}Query Example (Weaviate)
{
Get {
JobPost(
nearText: { concepts: ["software engineer"] }
where: {
operator: And
operands: [
{ path: ["locationCity"], operator: Equal, valueText: "Amsterdam" }
{ path: ["salaryMin"], operator: GreaterThan, valueNumber: 100000 }
]
}
limit: 5
) {
title
company
locationCity
salaryMin
salaryMax
}
}
}Analytics Query Example (ClickHouse)
SELECT query_tags['city'] AS city,
countIf(event_type = 'search') AS searches,
countIf(event_type = 'click') AS clicks,
round(clicks * 100.0 / searches, 2) AS ctr_percent
FROM analytics.events
GROUP BY city
ORDER BY ctr_percent DESC;Search Flow Example
Resume → Matching Jobs:
- Candidate uploads resume.
- Workflow parses, tags, embeds, and stores data.
- Weaviate nearObject query finds relevant jobs.
Natural Query → Matching Jobs:
- Query: “Software engineer jobs in Amsterdam paying 100K+”.
- LLM extracts: { role: “software engineer”, city: “Amsterdam”, salary_min: 100000 }.
- Hybrid search in Weaviate → filtered by Postgres.
Why This Works
- Semantic + structured search = higher match accuracy.
- Resilient orchestration = scraping & enrichment never stall.
- Fast analytics = insights on user behavior, skills demand, and scraping health.
- Privacy-aware = secure resume storage, anonymized analytics.
Final Thoughts
By combining scraping, LLM enrichment, hybrid vector search, and real-time analytics, this architecture delivers a production-ready AI job platform. Candidates get smarter recommendations, recruiters see better-fit applicants, and the platform continuously improves through feedback loops.